
This page walks you through a simple demonstration of how CockroachDB replicates, distributes, and rebalances data. Starting with a 3-node local cluster, you'll write some data and verify that it replicates in triplicate by default. You'll then add 2 more nodes and watch how CockroachDB automatically rebalances replicas to efficiently use all available capacity.
Before you begin
Make sure you have already installed CockroachDB.
Step 1. Start a 3-node cluster
Use the
cockroach startcommand to start 3 nodes:$ cockroach start \ --insecure \ --store=rep-node1 \ --listen-addr=localhost:26257 \ --http-addr=localhost:8080 \ --join=localhost:26257,localhost:26258,localhost:26259 \ --background$ cockroach start \ --insecure \ --store=rep-node2 \ --listen-addr=localhost:26258 \ --http-addr=localhost:8081 \ --join=localhost:26257,localhost:26258,localhost:26259 \ --background$ cockroach start \ --insecure \ --store=rep-node3 \ --listen-addr=localhost:26259 \ --http-addr=localhost:8082 \ --join=localhost:26257,localhost:26258,localhost:26259 \ --backgroundUse the
cockroach initcommand to perform a one-time initialization of the cluster:$ cockroach init \ --insecure \ --host=localhost:26257
Step 2. Write data
Use the
cockroach workloadcommand to generate an exampleintrodatabase:$ cockroach workload init intro \ 'postgresql://root@localhost:26257?sslmode=disable'Open the built-in SQL shell and verify that the new
introdatabase was added with one table,mytable:$ cockroach sql --insecure --host=localhost:26257> SHOW DATABASES;database_name +---------------+ defaultdb intro postgres system (4 rows)> SHOW TABLES FROM intro;table_name +------------+ mytable (1 row)> SELECT * FROM intro.mytable WHERE (l % 2) = 0;l | v +----+------------------------------------------------------+ 0 | !__aaawwmqmqmwwwaas,,_ .__aaawwwmqmqmwwaaa,, 2 | !"VT?!"""^~~^"""??T$Wmqaa,_auqmWBT?!"""^~~^^""??YV^ 4 | ! "?##mW##?"- 6 | ! C O N G R A T S _am#Z??A#ma, Y 8 | ! _ummY" "9#ma, A 10 | ! vm#Z( )Xmms Y 12 | ! .j####mmm#####mm#m##6. 14 | ! W O W ! jmm###mm######m#mmm##6 16 | ! ]#me*Xm#m#mm##m#m##SX##c 18 | ! dm#||+*$##m#mm#m#Svvn##m 20 | ! :mmE=|+||S##m##m#1nvnnX##; A 22 | ! :m#h+|+++=Xmm#m#1nvnnvdmm; M 24 | ! Y $#m>+|+|||##m#1nvnnnnmm# A 26 | ! O ]##z+|+|+|3#mEnnnnvnd##f Z 28 | ! U D 4##c|+|+|]m#kvnvnno##P E 30 | ! I 4#ma+|++]mmhvnnvq##P` ! 32 | ! D I ?$#q%+|dmmmvnnm##! 34 | ! T -4##wu#mm#pw##7' 36 | ! -?$##m####Y' 38 | ! !! "Y##Y"- 40 | ! (21 rows)Exit the SQL shell:
> \q
Step 3. Verify replication
To understand replication in CockroachDB, it's important to review a few concepts from the architecture:
Concept Description Range CockroachDB stores all user data (tables, indexes, etc.) and almost all system data in a giant sorted map of key-value pairs. This keyspace is divided into "ranges", contiguous chunks of the keyspace, so that every key can always be found in a single range.
From a SQL perspective, a table and its secondary indexes initially map to a single range, where each key-value pair in the range represents a single row in the table (also called the primary index because the table is sorted by the primary key) or a single row in a secondary index. As soon as that range reaches 64 MiB in size, it splits into two ranges. This process continues for these new ranges as the table and its indexes continue growing.Replica CockroachDB replicates each range (3 times by default) and stores each replica on a different node. With those concepts in mind, open the Admin UI at http://localhost:8080 and view the Node List:
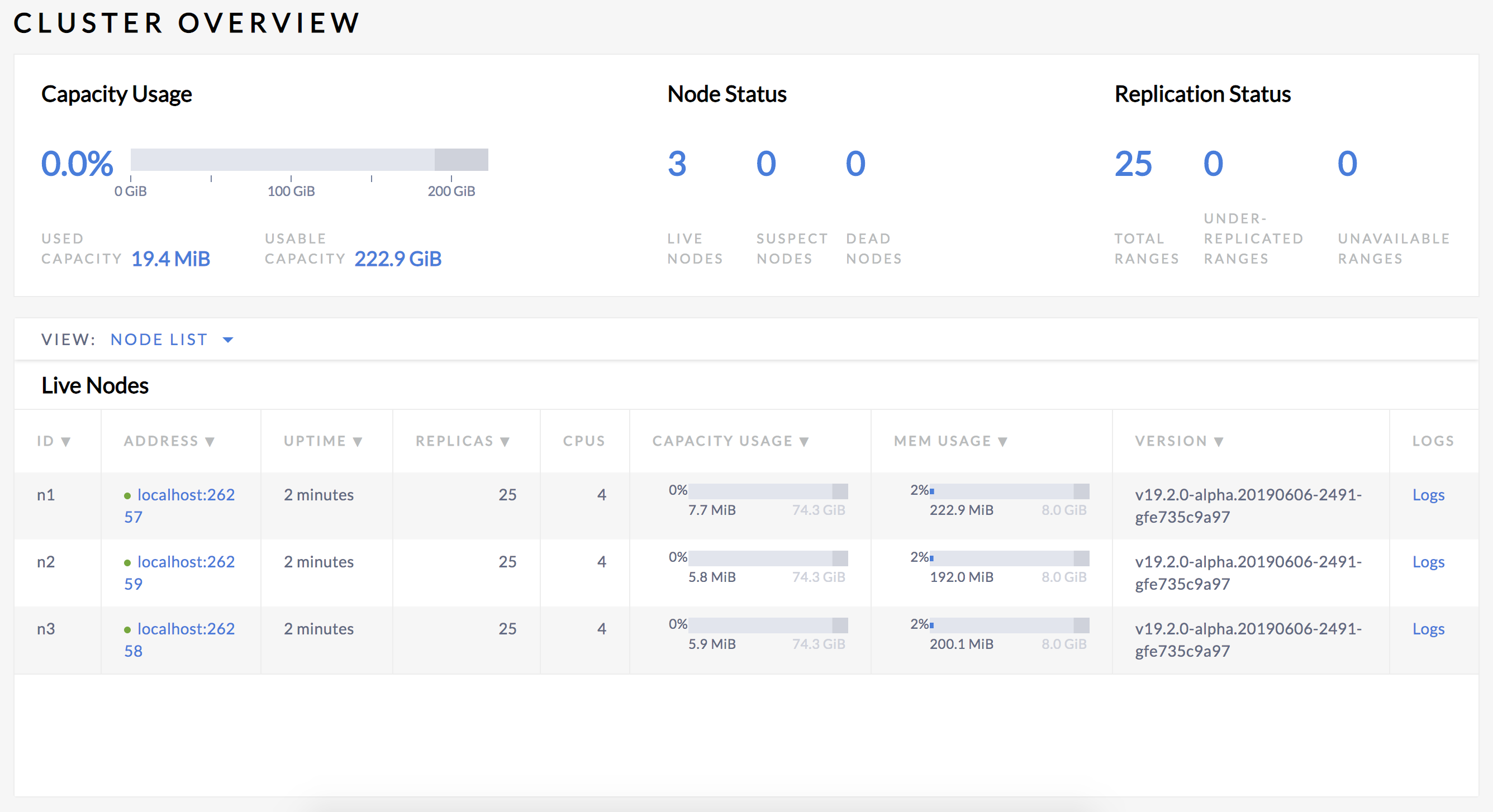
Note that the Replicas count is the same on all three nodes. This indicates:
- There are this many "ranges" of data in the cluster. These are mostly internal "system" ranges since you haven't added much table data.
- Each range has been replicated 3 times (according to the CockroachDB default).
- For each range, each replica is stored on different nodes.
Step 4. Add two more nodes
$ cockroach start \
--insecure \
--store=rep-node4 \
--listen-addr=localhost:26260 \
--http-addr=localhost:8083 \
--join=localhost:26257 \
--background
$ cockroach start \
--insecure \
--store=rep-node5 \
--listen-addr=localhost:26261 \
--http-addr=localhost:8084 \
--join=localhost:26257 \
--background
Step 5. Watch data rebalance
Back in the Admin UI, you'll see that there are now 5 nodes listed:
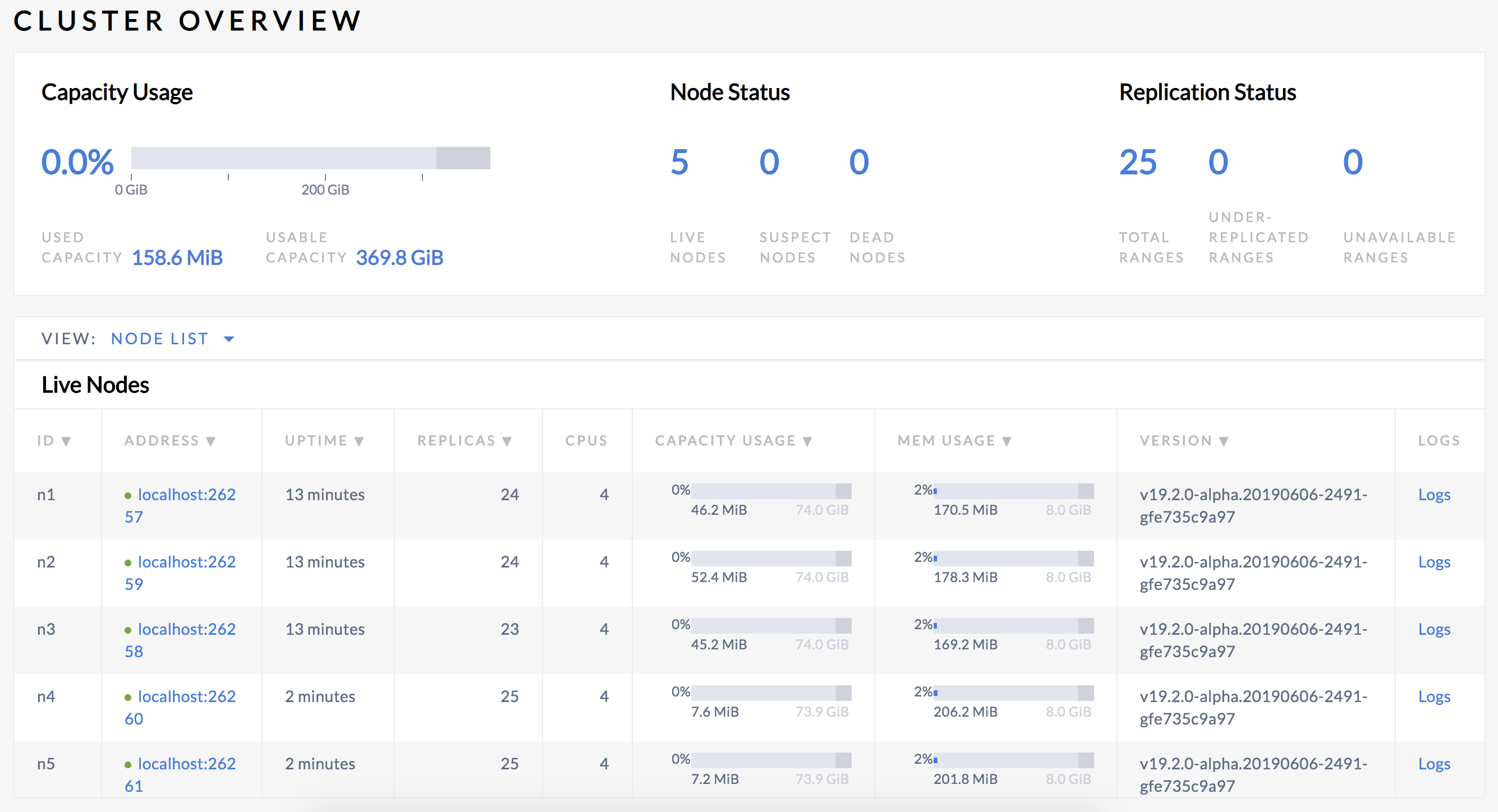
At first, the replica count will be lower for nodes 4 and 5. Very soon, however, you'll see those numbers even out across all nodes, indicating that data is being automatically rebalanced to utilize the additional capacity of the new nodes.
Step 6. Stop the cluster
When you're done with your test cluster, use the
cockroach quitcommand to gracefully shut down each node.$ cockroach quit --insecure --host=localhost:26257$ cockroach quit --insecure --host=localhost:26258$ cockroach quit --insecure --host=localhost:26259Note:For the last 2 nodes, the shutdown process will take longer (about a minute each) and will eventually force the nodes to stop. This is because, with only 2 of 5 nodes left, a majority of replicas are not available, and so the cluster is no longer operational.
$ cockroach quit --insecure --host=localhost:26260$ cockroach quit --insecure --host=localhost:26261To restart the cluster at a later time, run the same
cockroach startcommands as earlier from the directory containing the nodes' data stores.If you do not plan to restart the cluster, you may want to remove the nodes' data stores:
$ rm -rf rep-node1 rep-node2 rep-node3 rep-node4 rep-node5
What's next?
Explore other core CockroachDB benefits and features: